This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Results from BMC SAS scientists open up new treatment options for heart and muscle diseases
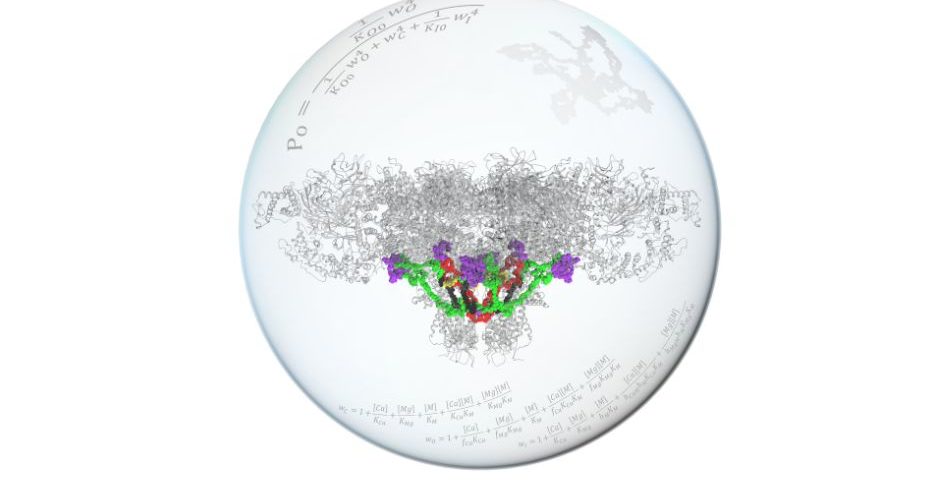
The function of the ryanodine receptor, an ion channel in cardiac and skeletal muscle cells, is controlled by binding divalent ions to their activation and inhibition sites. The figure shows a model of the molecular structure of the ryanodine receptor with allosteric pathways highlighted in color that connect the ion binding sites to the gates that open the channel. These structural interactions were transformed into a thermodynamic model of the channel function, shown by equations on the surface of a glass sphere.
An innovative approach to the analysis of complex biomolecules, which opens a new direction in the research of drugs that protect against sudden cardiac death, has been published these days by researchers from the Department of Cellular Cardiology of the Biomedical Research Center of the Slovak Academy of Sciences (BMC SAS), led by Alexandra Zahradnikova, in the top scientific journal PLOS Computational Biology.
“Our results address the relationship between the structure and function of complex biomolecules and provide a basic framework for understanding the role of ryanodine receptors in the regulation of muscle work in health and disease,” says lead author of the paper, Dr. Alexandra Zahradnikova.
“This allows us to explore a new avenue of research into drugs protecting us from certain types of sudden cardiac death or sudden anaesthesia-induced overheating of the body,” she adds.
The relationship between the structure and function of biomolecules is key to understanding their role in living organisms. Ryanodine receptors play a central role in the function of cardiac and skeletal muscles. Despite the wealth of experimental data generated in recent decades, the relationship between their structure and function has remained poorly understood, hindering the development of effective treatments for life-threatening cardiac and muscular diseases.
In this study, the researchers used state-of-the-art computational techniques to analyze published structures of cardiac and skeletal forms of ryanodine receptors, focusing on the regulation of their opening by calcium and magnesium ions.
They revealed activation and inhibition pathways that link the binding sites of these ions to molecular gates whose movement doses the amount of calcium ions in the cell according to the desired force of muscle work. They used the structural insights gained to create a molecular model of ryanodine receptor function that was able to reproduce the experimental observations of several independent laboratories.
The scientific journal PLOS Computational Biology presents papers of exceptional significance that advance our understanding of living systems by leveraging innovative computational methods, including artificial intelligence. It is located in the first decile in the Mathematics – Modeling and Simulation field according to the SCIMAGO database. The article is publicly available here: https://journals.plos.org/ploscompbiol/article?id=10.1371/journal.pcbi.1012950.
Text: Dr. I. Zahradník, BMC SAS; E. Rybárová, BMC SAS
Main photo: Alexandra Zahradníková and Ivan Zahradník, BMC SAS © CC-BY Creative Commons Attribution License
Photos at the end of the article: E. Rybárová, BMC SAV
- Dr. Alexandra Zahradníková, Head of the team of Cellular Cardiology, BMC SAS.
- From right Dr. Alexandra Zahradníková with her husband and co-author of the article Dr. Ivan Zahradník and daughter Alexandra Zahradníková Jr.










